Hip Dysplasia is partially a genetic disease, probably triggered by over feeding of large and giant breed puppies. The goal of reputable breeders should be to confine breeding to those pairs of canines that are at least free of hip dysplasia. A large investment in raising puppies to be bred must be made before The Orthopedic Foundation of America (OFA) X-ray diagnosis and certification of dogs can be made. That is because the exam can’t be conducted on animals younger than 2 years of age.
OFA Certification Exam Expensive, Dangerous
The OFA certification exam is not only expensive, it is dangerous to the animal to a certain degree. To test the dog, it must be placed in a very unusual position for the X-ray and this requires either full anesthesia or the use of powerful sedatives.
As with humans, general anesthesia can be dangerous, and especially so for dogs.
So, just how does the OFA determine if animals are suitable for breeding? All of the evaluation is focused on reading X-rays of the animal as conducted by specially trained veterinarians.
Avoiding Hip Dysplasia
But, since it has been shown that hip dysplasia seems to develop in part because of overfeeding, it is entirely possible to raise dogs to maturity without their developing any sign of dysplasia, despite having the genetic tendency. In this case, the OFA certification doesn’t guarantee genetically “clean” breeding pairs. All it shows is that EITHER the dogs are genetically clean, OR that they are not but have been carefully raised as recommended by many veterinarians and breeders. Also, they have not been given very rich, high calorie and high protein puppy food and nothing is known about their genetics.
In fact, to be absolutely certain of genetically pure animals, it would appear to be necessary to overfeed them.
What?
Yes, raise them so that if there is any tendency to develop hip bone structure problems, they will develop.
Otherwise it is difficult to see just what guarantee the OFA certification actually provides.
But certification is commonly done so let’s take a quick look at what the examination entails.
The positioning for the OFA test requires the animal to be positioned on his back with hind legs extended together nearly parallel to the table. OFA evaluation procedures.
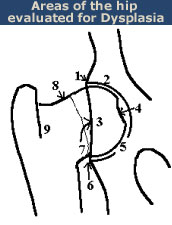
OFA Certification Hip Dysplasia evaluation diagram
The following areas are evaluated:
- Craniolateral acetabular rim.
- Cranial acetabular margin.
- Femoral head (hip ball).
- Fovea capitus (normal flattened area on hip ball).
- Acetabular notch.
- Caudal acetabular rim.
- Dorsal acetabular margin.
- Junction of femoral head and neck.
- Trochanteric fossa.
where the numbers refer to the image from the OFA Certification web site..
Only animals with Good, Fair, or Excellent ratings are given OFA ratings and considered suitable for breeding. Those evaluated with the four lowest grades are not given OFA Certification numbers.
If your Dog Has Hip Dysplasia
There are ways to support dogs with hip Dysplasia. Galia Weiss, an Israeli designer created a stylish harness to support dogs with this problem.
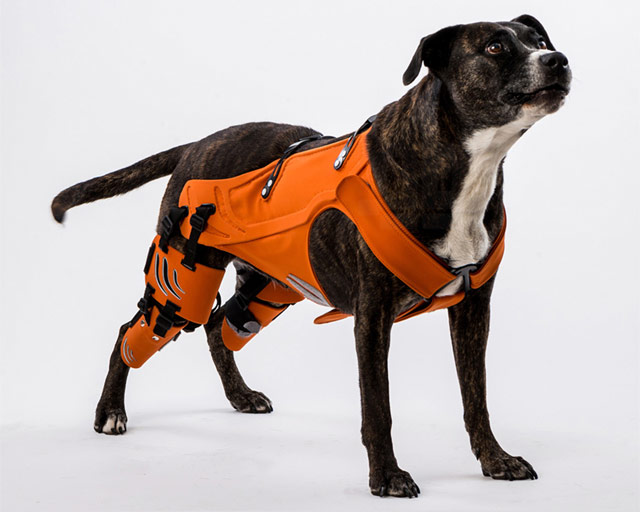

A special harness for dogs with hip dysplasia, designed by Galia Weiss






Recent Comments